EventBridge Scheduler
Introduction
Why EventBridge Scheduler
Before we mostly relied on CloudWatch Event rules to schedule tasks it worked, but it was limited no one-time schedules, no payload flexibility, and not great for managing thousands of tasks.
EventBridge Scheduler changes the game:
- It can handle millions of schedules
- Supports both one-time and recurring invocations
- Invokes over 270 AWS services or even external APIs
- Has fine-grained retry, encryption, and delivery window controls
- And fully serverless Zero cron servers, Zero EC2 instances

Amazon EventBridge Scheduler offers key features that make scheduling simple and reliable. We can use templated targets for quick setup of common operations, or universal targets for custom triggers across AWS services. Flexible time windows let us spread out schedules when exact timing isn't critical, while built-in retries ensure our tasks execute successfully even if there are temporary failures.
Schedule Types
When we're setting up schedules in EventBridge Scheduler, we have the flexibility to define them using three different expression types as showing in the table bellow
| Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| at(2025-12-01T10:00:00Z) | one-time | Run exactly once |
| cron(0 12 * * ? *) | every day at 12:00 UTC | Full cron power |
| rate(5 minutes) | every 5 minutes | Simple repetition |
This gives us the control to choose the scheduling method that best fits our specific use case, throughout the rest of this post, we'll explore each of these expression types in detail.
Create EventBridge Schedule
When creating a schedule, vai the console after entering the name and description, we need to choose the schedule pattern as shown in the image below
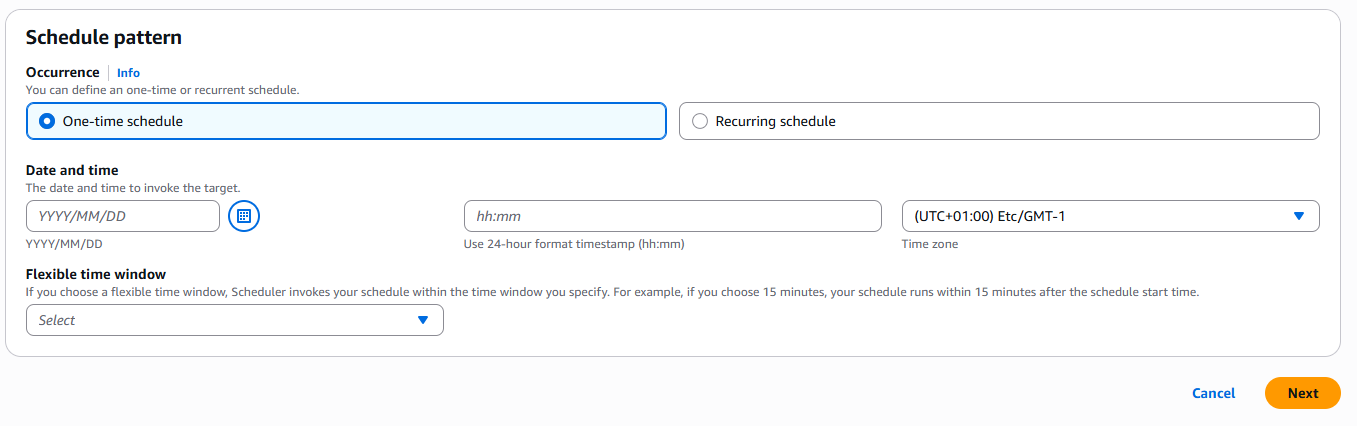
As we can see, we have 2 patterns: one-time schedule and recurring schedule (cron + rate), for the one-time option, it's simple we just need to specify the date, time, time zone, and the flexible time window
For the recurring option, we need to choose between a cron-based schedule or a rate-based schedule, then enter the corresponding cron expression or rate expression.
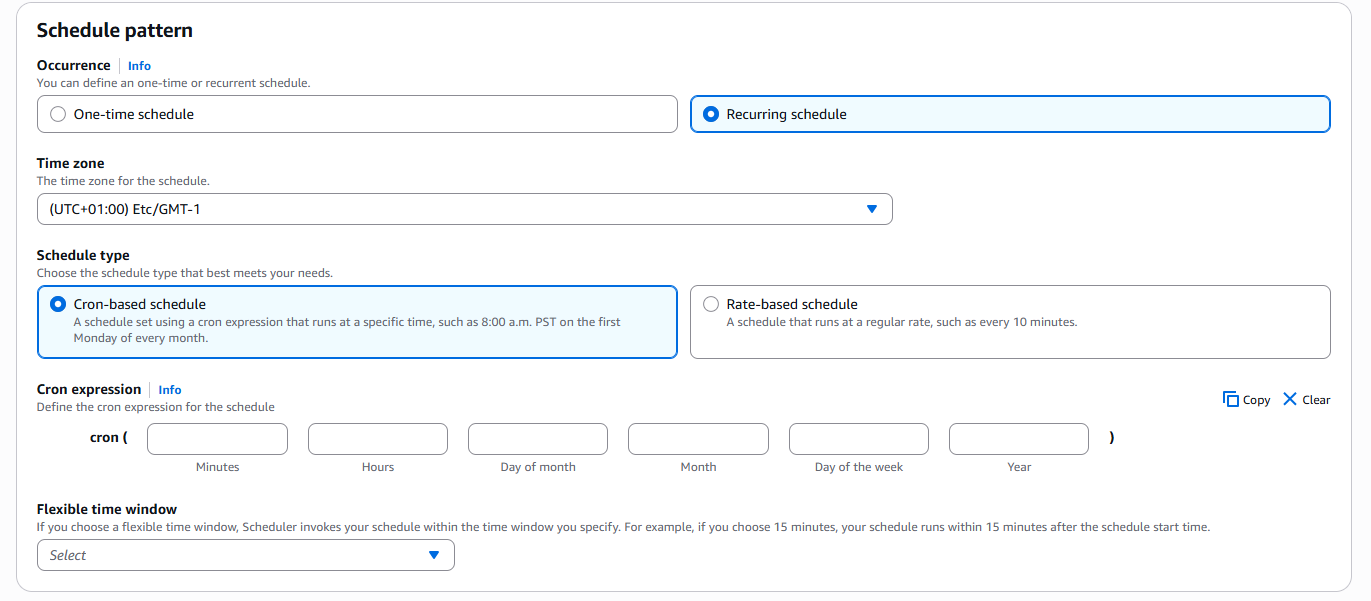
cron-based schedule
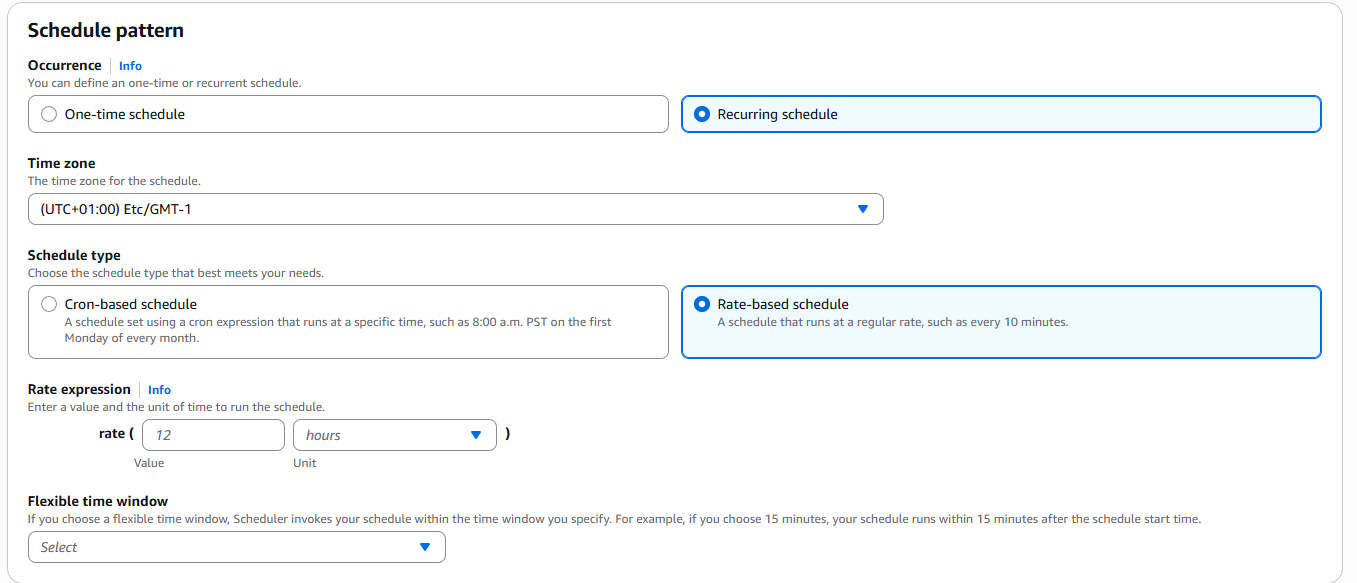
rate-based schedule
The next step is selecting a target. In this case, I've chosen an AWS Lambda function to demonstrate the process
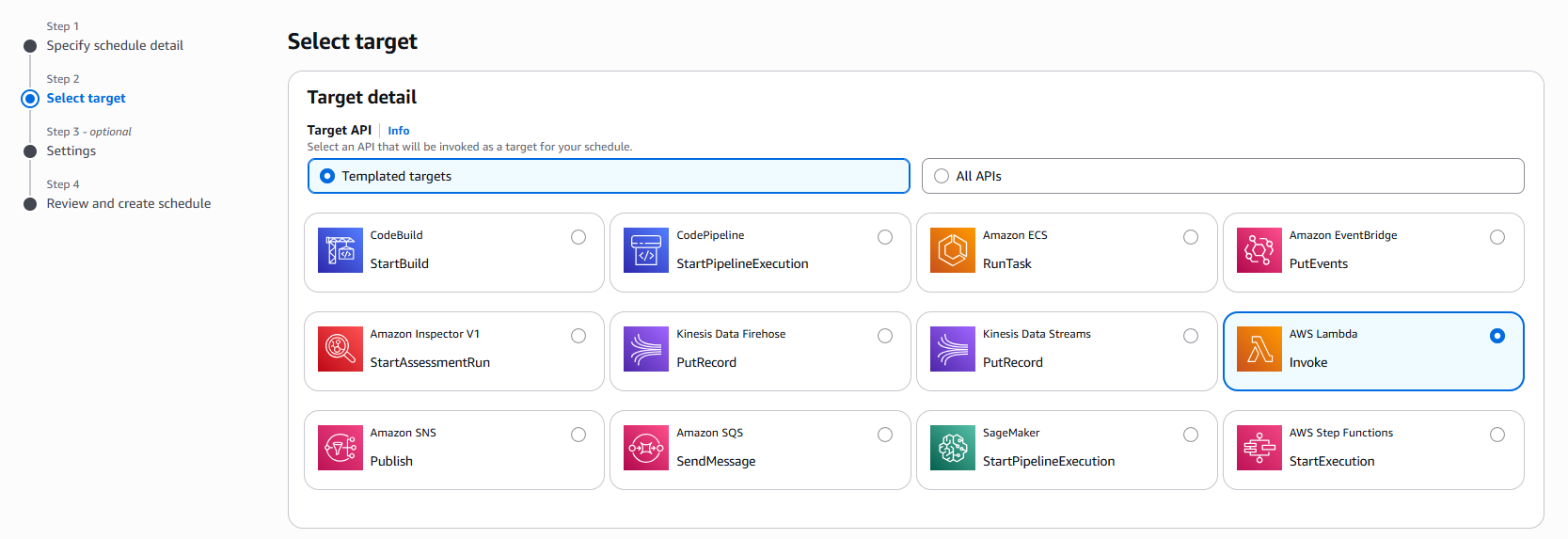
Schedule Target
Then we select the Lambda function we want to trigger. We can also specify a JSON payload, which can be helpful in certain situations where we need to pass specific data to our function
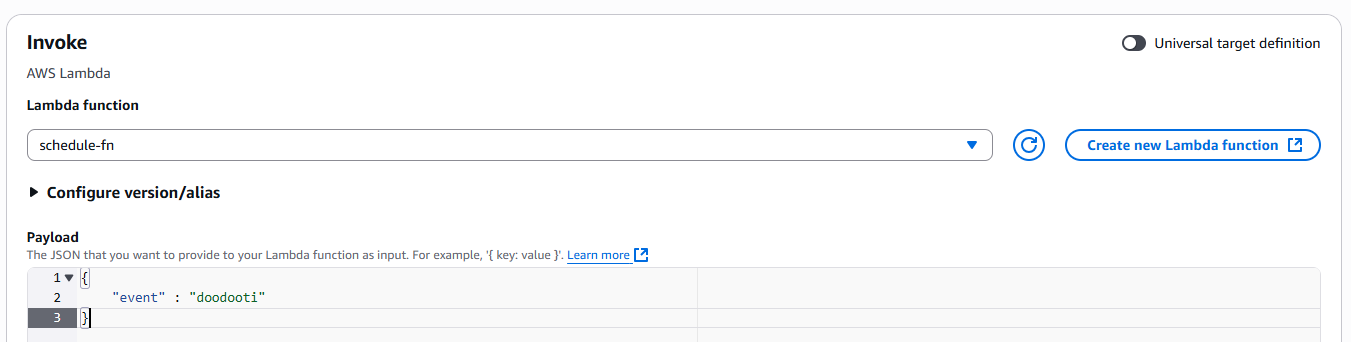
Function and Payload
With that, our configuration is complete and the schedule is ready to execute. keep in mind that the scheduler needs permission to invoke our function, which is handled automatically by AWS when we create the schedule through the console.
Using the Node.js SDK
// install the sdk
npm install @aws-sdk/client-scheduler
// define the client
const client = new SchedulerClient({ region: "us-east-1" });One-Time Schedule
async function scheduleOrderProcessing(orderId, runAt) {
const command = new CreateScheduleCommand({
Name: `process-order-${orderId}`,
ScheduleExpression: `at(${runAt})`,
FlexibleTimeWindow: { Mode: 'OFF' },
Target: {
Arn: 'arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:processOrder',
RoleArn: 'arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/EventBridgeSchedulerRole',
Input: JSON.stringify({ orderId }),
},
});
const response = await client.send(command);
console.log(`📦 Schedule created for order ${orderId} at ${runAt}`);
}This function creates a one-time EventBridge schedule to trigger a Lambda function at a specific time. It takes an orderId and runAt timestamp as parameters, then uses the CreateScheduleCommand to set up the schedule with a unique name based on the order ID. The schedule uses the at() expression for one-time execution, targets a specific Lambda function with the necessary IAM role permissions, and passes the orderId as JSON input through the Input field. This payload will be available to our Lambda function when it executes, allowing it to know which order to process
Cron-based Schedule
async function createDailyReportSchedule() {
const command = new CreateScheduleCommand({
Name: 'daily-report',
Description: 'Generate a daily report at 6 AM Tunis time',
ScheduleExpression: 'cron(0 6 * * ? *)',
ScheduleExpressionTimezone: 'Europe/Tunis',
FlexibleTimeWindow: { Mode: 'OFF' },
Target: {
Arn: 'arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:generateDailyReport',
RoleArn: 'arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/EventBridgeSchedulerRole',
Input: JSON.stringify({ type: 'daily' }),
},
});
const response = await client.send(command);
console.log('✅ Schedule created:', response);
}This function creates a recurring schedule that runs every day at 6 AM using a cron expression. It triggers a Lambda function to generate reports and passes type: "daily" as input to specify the report type.
Rate-based Schedule
For the rate-based scheduler, it's the same process. We just need to change the ScheduleExpression from a cron expression to a rate expression
async function createHourlyReportSchedule() {
const command = new CreateScheduleCommand({
Name: 'hourly-report',
Description: 'Generate a report every hour',
ScheduleExpression: 'rate(1 hour)',
FlexibleTimeWindow: { Mode: 'OFF' },
Target: {
Arn: 'arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:generateDailyReport',
RoleArn: 'arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/EventBridgeSchedulerRole',
Input: JSON.stringify({ type: 'hourly' }),
},
});
const response = await client.send(command);
console.log('✅ Schedule created:', response);
}Retry policy, DLQ and Reliability
EventBridge Scheduler allows us to configure retry behavior for failed invocations and we can customize:
- Max attempts
- Backoff strategy
- Dead Letter Queue (DLQ) for debugging
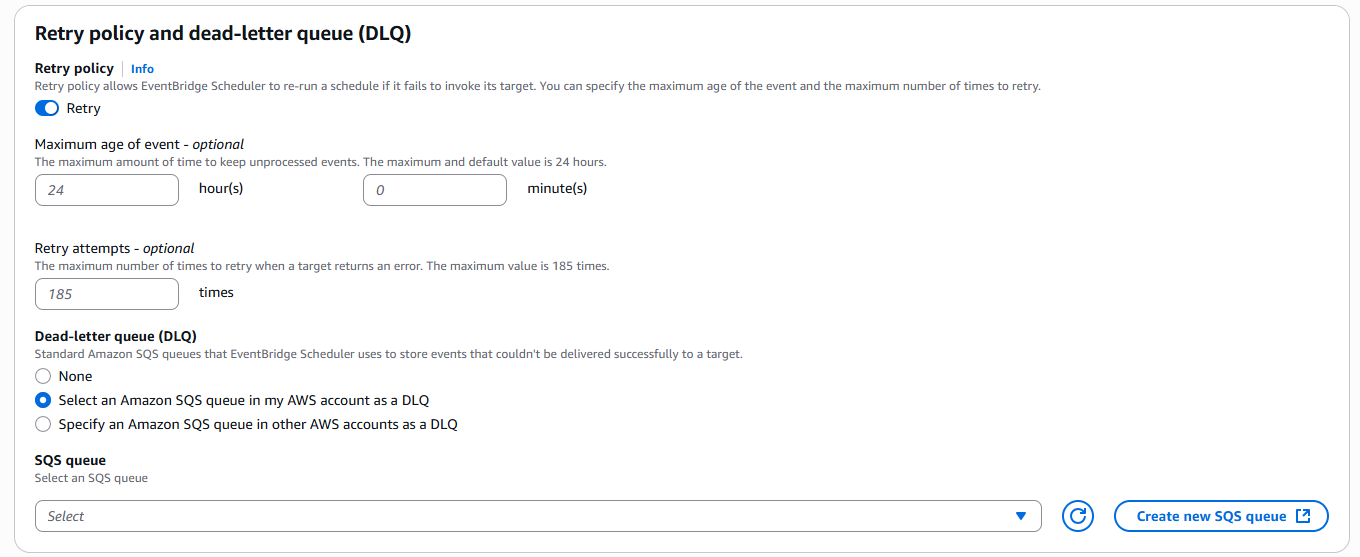
Retry policy and dead-letter queue (DLQ)
This ensures our tasks are idempotent, meaning even if the same schedule runs twice due to retries, our logic should handle it safely.
Best practice: Use a lightweight Lambda as a trigger and enqueue jobs into SQS or Step Functions for the real work. That way, the Scheduler never overloads our main services.
Common Patterns
Here are a few ways teams use it in production:
- Daily report generation: Scheduler → Lambda → S3 → SNS notification
- Time-based workflow orchestration: Scheduler → Step Functions → Multi-step business flow
- Webhook / API calling: Scheduler → API Destination → External system
- Deferred retries: Scheduler → one-time "retry later" Lambda trigger
Important Considerations
- If we use very frequent schedules (like every minute for thousands of items), costs can pile up fast consider batching.
- Each schedule name must be unique. Use IDs or timestamps in names for one-time jobs.
- Cron timezones can be tricky always test with UTC first, then apply ScheduleExpressionTimezone.
- Delete schedules we no longer need they persist until removed.
Conclusion
EventBridge Scheduler is one of those AWS services that feels like a small feature but solves a huge pain. No more EC2 cron daemons, no more Lambda self-invocation hacks, no more sleep queue patterns
It's clean, scalable, and beautifully simple the kind of AWS service we can just set and forget
